Bernadus sutomo T
Ega Prasetyo
Firwan Setiawan
by : Pamulang University
Indirect Questions
Formula
Yes/No question : Introductory clause + if / whether + S + V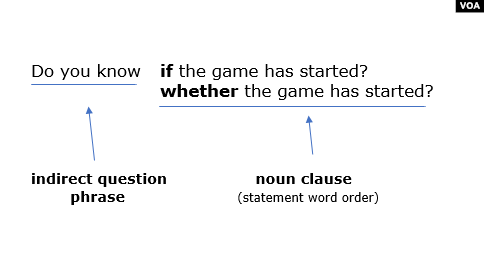 Have a look at this conversation.
Have a look at this conversation.
Me: Excuse me. Could you tell me where the nearest station is?
Person in the street: Certainly. It's along that road on the right.
Me: Thank you. And do you know if there's a supermarket near here?
Person in the street: Yes, there's one next to the station.
Me: Thank you very much for your help.
I use indirect questions when I'm asking for help in the street, because
they are very polite. Indirect questions start with a phrase like
'could you tell me...' or 'do you know...'. For example:
Direct question: Where is the bank?
Indirect question: Could you tell me where the bank is?
Notice that in the indirect question I put the verb ('is') after the
subject ('the bank'), in the same way as I do with a normal positive
sentence ('the bank is over there'), but in the direct question I put
the verb 'is' before the subject 'the bank'. This is called inversion,
and it is used to make direct questions in many verb tenses in English,
but we don't use inversion in indirect questions. This is very similar
to the grammar of reported questions. However, we use indirect questions
in a different way from reported questions. Indirect questions are a
way of being polite. They are very, very common in English, especially
when you're talking to someone you don't know.
'Yes / No' Questions
To make an indirect 'yes / no' question, we use 'if' and the word order
of a normal positive sentence. This is the same as for reported 'yes /
no' questions. On the other hand, we don't usually need to 'backshift'
(change the tense of the verb) as we do with reported questions.
Of course, most tenses make questions by using 'inversion' (changing the
word order). To change from a direct 'yes / no' question with inversion
to an indirect question, you add 'if' and change the word order back to
a normal positive sentence. You don't need to use inversion.
'Yes / no' questions for tenses with inversion:
| Verb Tense | Direct Question | Indirect Question |
| Present simple with 'be' | Is he Spanish? | Can you tell me if he is Spanish? |
| Present continuous | Is the restaurant closing now? | Can you tell me if the restaurant is closing now? |
| Past simple with 'be' | Was he late for the meeting? | Can you tell me if he was late for the meeting? |
| Past continuous | Were you watching TV at 3pm? | Can you tell me if you were watching TV at 3pm? |
| Present perfect | Has Lucy been to Mexico? | Can you tell me if Lucy has been to Mexico? |
| Present perfect continuous | Has she been living here long? | Can you tell me if she has been living here long? |
| Past perfect | Had she found this job when she moved here? | Can you tell me if she had found this job when she moved here? |
| Past perfect continuous | Had she been living here long when she met you? | Can you tell me if she had been living here long when she met you? |
| Future simple with 'will' | Will she start her new job next week? | Can you tell me if she will start her new job next week? |
| Future simple with 'going to' | Is it going to rain later? | Can you tell me if it is going to rain later? |
| Future continuous | Will Lisa be meeting the boss later? | Can you tell me if Lisa will be meeting the boss later? |
| Future perfect | Will he have finished the report by tonight? | Can you tell me if he will have finished the report by tonight? |
| Future perfect continuous | Will he have been studying French for twenty years when he retires? | Can you tell me if he will have been studying French for twenty years when he retires? |
| Modal verbs | Should we start now? | Can you tell me if we should start now? |
'Yes / no' questions with tenses that use 'do / does / did':
Sometimes you want to make an indirect question using the present simple
of any verb except 'be' or the past simple of any verb except 'be'.
These tense make direct questions by using 'do / does / did'. When we
want to make indirect 'yes / no' questions using these tenses, we need
'if' and we don't need 'do / does / did'.
| Verb Tense | Direct Question | Indirect Question |
| Present simple with any verb except 'be' | Does David live in London? | Can you tell me if David lives in London? |
| Past simple with any verb except 'be' | Did Amanda call John yesterday? | Can you tell me if Amanda called John yesterday? |
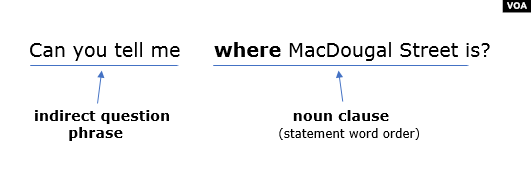
'Wh' Questions
In the same way as with reported 'wh' questions, we use the question
word and the word order of a normal positive sentence to make indirect
'wh' questions. We don't need to use inversion. Again, we also don't
usually need to 'backshift' (change the tense of the verb) as we do with
reported questions.
To change a direct question to an indirect question for tenses that make
questions using inversion, you just add 'if' and change the word order
back to a normal positive sentence.
Wh question : Introductory Clause + Wh word + S + V
 'Wh' questions for tenses with inversion:
'Wh' questions for tenses with inversion:
| Verb Tense | Direct Question | Indirect Question |
| Present simple with 'be' | Why is he unhappy? | Can you tell me why he is unhappy? |
| Present continuous | When is the restaurant closing? | Can you tell me when the restaurant is closing? |
| Past simple with 'be' | Why was he late for the meeting? | Can you tell me why he was late for the meeting? |
| Past continuous | What were you doing at 3pm? | Can you tell me what you were doing at 3pm? |
| Present perfect | Where has Lucy been? | Can you tell me where Lucy has been? |
| Present perfect continuous | How long has she been living here? | Can you tell me how long she has been living here? |
| Past perfect | Why had she quit her job before she moved here? | Can you tell me why she had quit her job before she moved here? |
| Past perfect continuous | How long had she been living here when she met you? | Can you tell me how long she had been living here when she met you? |
| Future simple with 'will' | When will she start her new job? | Can you tell me when she will start her new job? |
| Future simple with 'going to' | When is it going to rain? | Can you tell me when it is going to rain? |
| Future continuous | What time will Lisa be meeting the boss? | Can you tell me what time Lisa will be meeting the boss? |
| Future perfect | When will he have finished the report? | Can you tell me when he will have finished the report? |
| Future perfect continuous | How long will he have been studying French when he retires? | Can you tell me how long he will have been studying French when he retires? |
| Modal verbs | What should we do now? | Can you tell me what we should do now? |
'Wh' questions for tenses with 'do / does / did':
Sometimes you want to make an indirect 'wh' question using the present
simple of any verb except 'be' or the past simple of any verb except
'be'. Usually these tenses make questions by using 'do / does / did'.
However, when we want to make indirect 'wh' questions using these
tenses, we don't need 'do / does / did'. Instead, we use a question word
and then normal positive sentence word order.
| Verb Tense | Direct Question | Indirect Question |
| Present simple with any verb except 'be' | Where does David live? | Can you tell me where David lives? |
| Past simple with any verb except 'be' | Why did Amanda call John yesterday? | Can you tell me why Amanda called John yesterday? |
Common Problems
It can be difficult to remember to put the verb after the subject,
especially when the indirect question is in the present simple tense of
'be'. For example, we need to say:
Could you tell me where the station
is?
INDIRECT STATEMENT
What IS an INDIRECT STATEMENT?
You are used to most of the sentences you've ever seen so far being DIRECT STATEMENTS:
"My brother was looking for his dog"
"We will arrive tomorrow"
"Dinner is ready"
An INDIRECT STATEMENT
gives a 'reported' or 'second-hand' version, phrased as if someone else
has told you about it (or you have said or thought it to yourself):
I saw that my brother was looking for his dog
Our friends said that they would arrive tomorrow
Mother shouted that dinner was ready
II. it is best to work for as few companies as possible I dissagree, because, companies need employees with capacities that are in accordance with what the company needs, usually companies need a lot of employees if the desired target to achieve greater profits than the cost of expenditure. to reach the target, of course, the company needs employees who are in accordance with the field owned by the employee where they are placed at work. but if the company already feels enough that it only requires employees who are few but capable of competitiveness with large profits, sometimes the employees owned are quite few as long as they can achieve effective and efficient target.
I dissagree, because, companies need employees with capacities that are in accordance with what the company needs, usually companies need a lot of employees if the desired target to achieve greater profits than the cost of expenditure. to reach the target, of course, the company needs employees who are in accordance with the field owned by the employee where they are placed at work. but if the company already feels enough that it only requires employees who are few but capable of competitiveness with large profits, sometimes the employees owned are quite few as long as they can achieve effective and efficient target.



